
The results for British standard cable are calculated from BS7671 (18th Edition) Requirements for Electrical Installation, IEE Wiring Regulations, and are based on 230V and 415V voltage drop. Complete the sections below to calculate your results. For example, we can calculate the electrical resistance of an electric bulb that is installed in a room using the formula R = P/V 2.Eland Cables' Cable Calculator can help you determine the most appropriate cable size for your installation against British and IEC standards. To determine the electrical resistance of a component, it is possible to use the formulas derived from the combination of Watt’s law and Ohm’s law. It is possible to determine the voltage of an electrical component by using Watt’s formula (V=P/I) when you know the power and current of the component.ĥ. It is possible to determine the current of an electrical component by using Watt’s formula (I=P/V) when you know the power and voltage of the component.Ĥ. A building’s power requirements are determined by determining the individual power ratings of all the electrical appliances or components it will contain and adding them together.ģ. Additionally, it is possible to estimate the electricity costs associated with the system. This information can be used to determine the wire size that is suitable for your building. It is important to estimate the whole building’s power requirement when designing its wiring. Watt’s formula can be used to calculate the power requirements of a building. In order to calculate the power requirement, you need to multiply the current and voltage.Ģ. It can also be used to determine the power requirements of an individual component. You can use this formula to determine the actual amount of power that is generated by a power source. Here are a few applications of Watt’s lawġ. Several other formulas can also be derived from these formulas. By substituting these into Watt’s formula, we obtain It is a well-known fact that Ohm’s law states that I = V/R and V = IR. These laws can, however, be combined to produce useful formulas. Watt’s law describes the relationship between power, voltage, and current in a circuit, whereas Ohm’s law describes the relationship between resistance, voltage, and current. What is the difference between Watt’s law and Ohm’s law? Therefore, if we substitute the values, we obtain 0.273 Amperes of current. The voltage and power of the bulb are therefore 110V and 30W, respectively. When a light bulb is powered by 110 volts and has a power rating of 30 watts, what is the overall current? By using Watt’s law, one can determine the voltage, power, ampere, and resistance of an electrical circuit. Watt’s law has many practical applications. In simplest terms, power is the amount of energy transferred per unit time. In a circuit, power refers to the amount of work that can be performed or consumed by a component in a unit time. According to Ohm’s law, the amount of current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to its voltage, i.e., I = V/R It is measured in ohms (Ω).Ĭurrent, voltage, and resistance are related according to Ohm’s law. The resistance of an electrical component is a measure of its ability to resist the flow of current.

Resistance (R) is defined as the opposition offered by the circuit to the flow of current. There must be a difference in the potential for current to flow. It is a measure of how much electric charge is flowing through a given point in a circuit at any given time. Electric current will flow from a point of higher potential to a point of lower potential. In an electric circuit, the voltage (V) represents the difference in potential between two points.

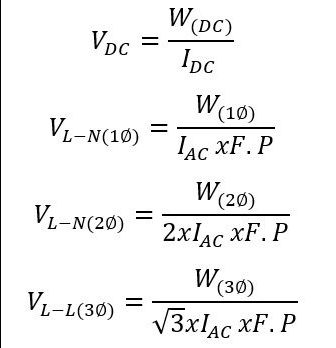
Where, P is power, V is voltage, and I is electric current


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
